Gait pattern is a series of rhythmical, alternating movement of trunk and limbs which results in forward progression of COG (center of gravity).
It is defined as human locomotion achieved by coordinated muscle work.
It is bi-phasic forward propulsion of COG of human body.
In simple words, gait pattern is the style of walking.
PHASES
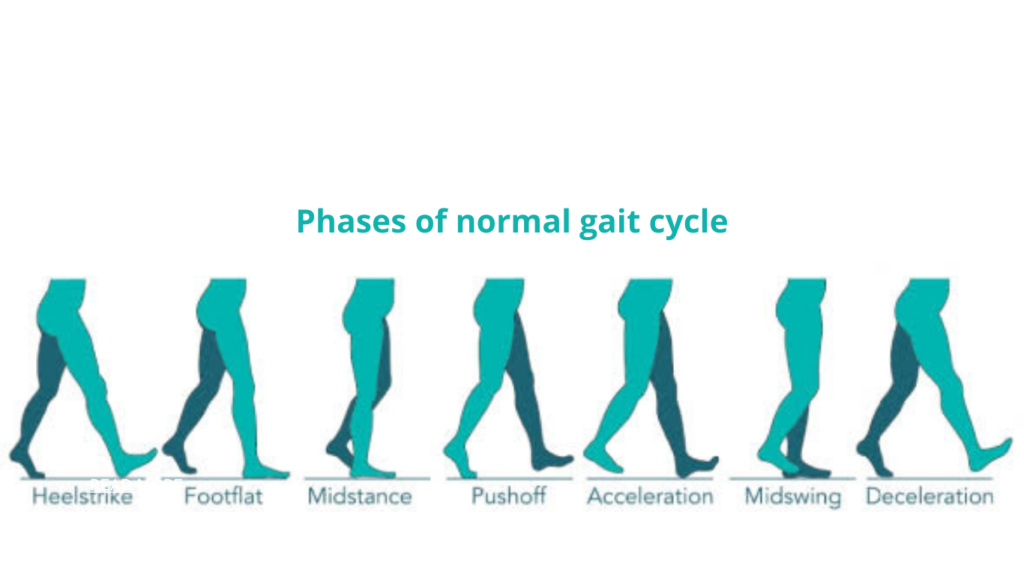
A gait cycle is the cyclic pattern of the movements that occur during walking. It is completed with two successive events of the same extremity.
During one cycle each extremity passes through two major phases :
- STANCE PHASE
- SWING PHASE
Each of the phases again go through some sub phases to complete the gait cycle.
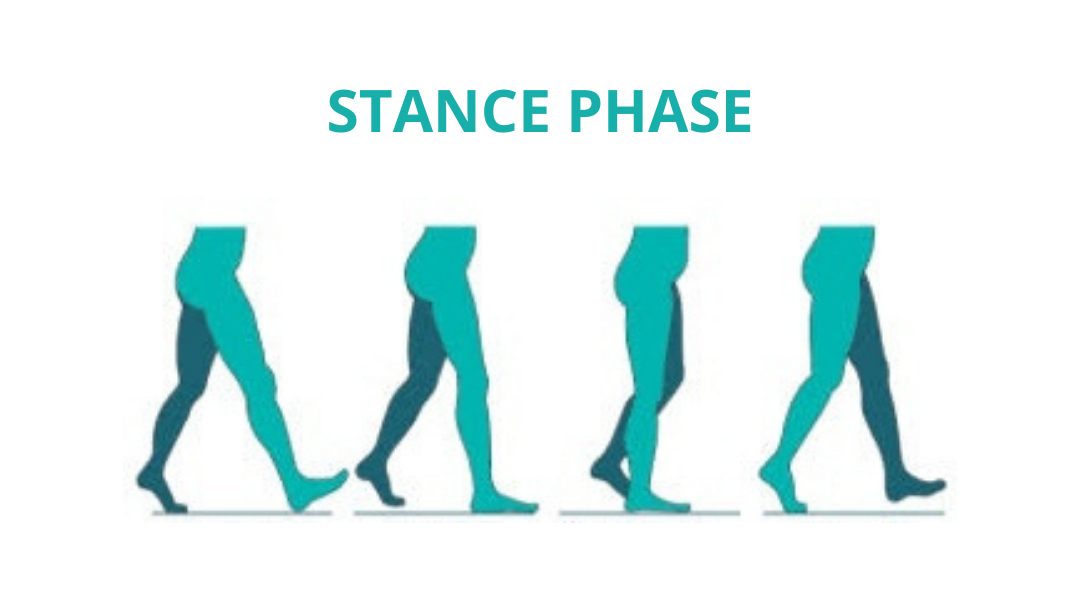
STANCE PHASE
- HEEL STRIKE
- FOOT FLAT
- MID STANCE
- HEEL OFF (PUSH OFF)
- TOE OFF (PUSH OFF)
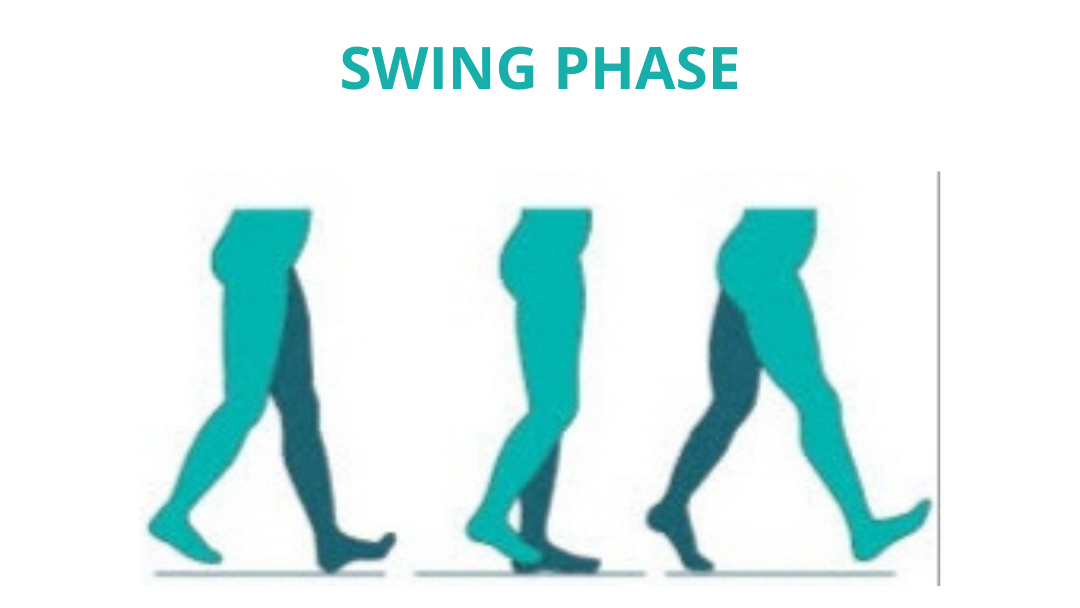
SWING PHASE
- EARLY SWING
- MID SWING
- LATE SWING
JOINT RANGE OF MOTION DURING GAIT PATTERN
For a normal walking, we need to maintain range of motion around hip joint, knee joint and ankle joint.
HIP JOINT – ROM approximately 20 degree extension to 20 degree flexion.
KNEE JOINT – ROM approximately 0 degree to 60 degree flexion.
ANKLE JOINT – ROM approximately 25 degree planter flexion to 7 degree dorsiflexion.
But it changes from phase to phase as follows
STANCE PHASE
HEEL STRIKE (INITIAL CONTACT)
Hip : 20 degree flexion
Knee : 0 degree flexion
Ankle : 0 degree planter flexion
FOOT FLAT
Hip : 15 degree flexion
Knee : 15 degree flexion
Ankle : 5 degree planter flexion
MID STANCE
Hip : 0 degree flexion
Knee : 5 degree flexion
Ankle : 5 degree planter flexion
HEEL OFF
Hip : 10-20 degree hyperextension
Knee : 0 degree flexion
Ankle : 0 degree planter flexion
TOE OFF
Hip : 10-20 degree hyperextension
Knee : 30 degree flexion
Ankle : 20 degree planter flexion
SWING PHASE
EARLY SWING
Hip : 20 degree flexion
Knee : 60 degree flexion
Ankle : 10 degree planter flexion
MID SWING
Hip : 30 degree flexion
Knee : 30 degree flexion
Ankle : 0 degree planter flexion
LATE SWING
Hip : 30 degree flexion
Knee : 0 degree flexion
Ankle : 0 degree planter flexion
REASONS FOR ABNORMAL GAIT PATTERN
Some pathology affects the normal pattern. It may be due to any joint deformity, lack of muscular strength, weakness, loss of motor function, pain, musculoskeletal or neuro-muscular cause.
Age is also a factor. As the age increases, walking speed declines. Step length getting shorter and slower cadence.
TYPE OF ABNORMAL GAIT PATTERNS
ANTALGIC GAIT
It is one of the most common forms of altered gait in patients presenting to the emergency department and primary care offices. patient complains –
- Pain in any lower extremity
- Result in shorter step length and lower stance time.
- Result in limping
TRENDELENBURG GAIT (hip abductor weakness)
- Excessive drop of contralateral hip in standing
- Compensated gait by trunk lean laterally towards the stance lower extremity of weak side.
ATAXIC GAIT (cerebellar)
It can be described as two types :
CEREBELLAR ATAXIA
- Stance and gait appeared in broad base
- Insecure and wobble walking
- Leg movement and step length are irregular and variable.
Walking style should be like:
- Compensate lateral body sway by walking causiously, stooping slightly and steadily the stance foot by bending the hip.
- Ataxia increase by complexity of the gait task like tendon walking and walking on uneven surface.
SENSORY ATAXIA
- Proprioception is effected (disturbance of body presentation)
- Stance and gait are broad and insecure
- The step length get shorten
- Sometimes feet are fifted and gait may be stompping quality
- Romberg’s test is positive.
HEMIPLEGIC GAIT (circumductory or spastic gait)
- Leg is held stiffly and abducted with each step and swung around to the ground in front, forming a semicircle
- It results from poor control of flexor muscles during swing phase
- Spasticity of extensor muscles acting to lengthen the affected leg
- Ankle is abnormally flexed downward and inward
- Initial contact during stance phase is abnormal
- Knee becomes stiff, hyper extends during stance, and does not flex normally during swing
PARKINSONIAN GAIT (propulsive/ fascinating)
- Typically this is found in Parkinson’s patient
- Brady kinetic, short, shuffling.
- Difficulty in initiation and stoppage
- Typically rigid akinetic gait impairement, which includes slow, narrow base and forward stoop posture
- Posture involving neck, shoulder and trunk bend.
- Feet are lifted less than normal, which may lead to shuffling.
HAND TO KNEE GAIT (knee extensor weakness)
- Weakness of quadriceps muscle lead to knee buckling in stance which is compensated by genu recurvature with help of upper limb by pressing the knee backward.
- An associated anterior trunk lean in the early part of stance, lead to keep the knee in extension without help of the knee extensor muscles.
Any assessment of lower limb must include gait pattern assessment. Musculoskeletal pathology tends to modify walking pattern because of muscle weakness, pain or altered ROM.
Nicely explained.. CAN U PLEASE EXPLAIN ABOUT “PAIN GATE THEORY” in next article?
Pingback: Parkinson's Disease : A Quick Overview - Physiofitfinder
Excellent post. I was checking continuously this blog and I am impressed.
Great post I must say.. Simple yet somehow intriguing, notable and engaging.. Continue the awesome work!
Thanks for taking the time to discuss this, I really feel strongly about it and love learning extra on this topic. If attainable, as you achieve experience, would you thoughts updating your blog with additional data? It is extremely useful for me.
Many thanks for making the effort to discuss this, I feel strongly about this and enjoy studying a great deal more on this matter. If possible, as you gain expertise, would you mind updating your webpage with a great deal more details? It’s extremely beneficial for me.
Universitas Bermutu
https://medium.com/@AriBautist93573/бесплатный-vps-на-ubuntu-linux-08983b2540cd
VPS SERVER
Высокоскоростной доступ в Интернет: до 1000 Мбит/с
Скорость подключения к Интернету — еще один важный фактор для успеха вашего проекта. Наши VPS/VDS-серверы, адаптированные как под Windows, так и под Linux, обеспечивают доступ в Интернет со скоростью до 1000 Мбит/с, что гарантирует быструю загрузку веб-страниц и высокую производительность онлайн-приложений на обеих операционных системах.
VPS SERVER
Высокоскоростной доступ в Интернет: до 1000 Мбит/с
Скорость подключения к Интернету — еще один важный фактор для успеха вашего проекта. Наши VPS/VDS-серверы, адаптированные как под Windows, так и под Linux, обеспечивают доступ в Интернет со скоростью до 1000 Мбит/с, что гарантирует быструю загрузку веб-страниц и высокую производительность онлайн-приложений на обеих операционных системах.
Just got my first cavity. Fairly disastrous. I would like a excellent smile. Hunting more solutions. Thank you for the write-up